Orthogonal bracket¶
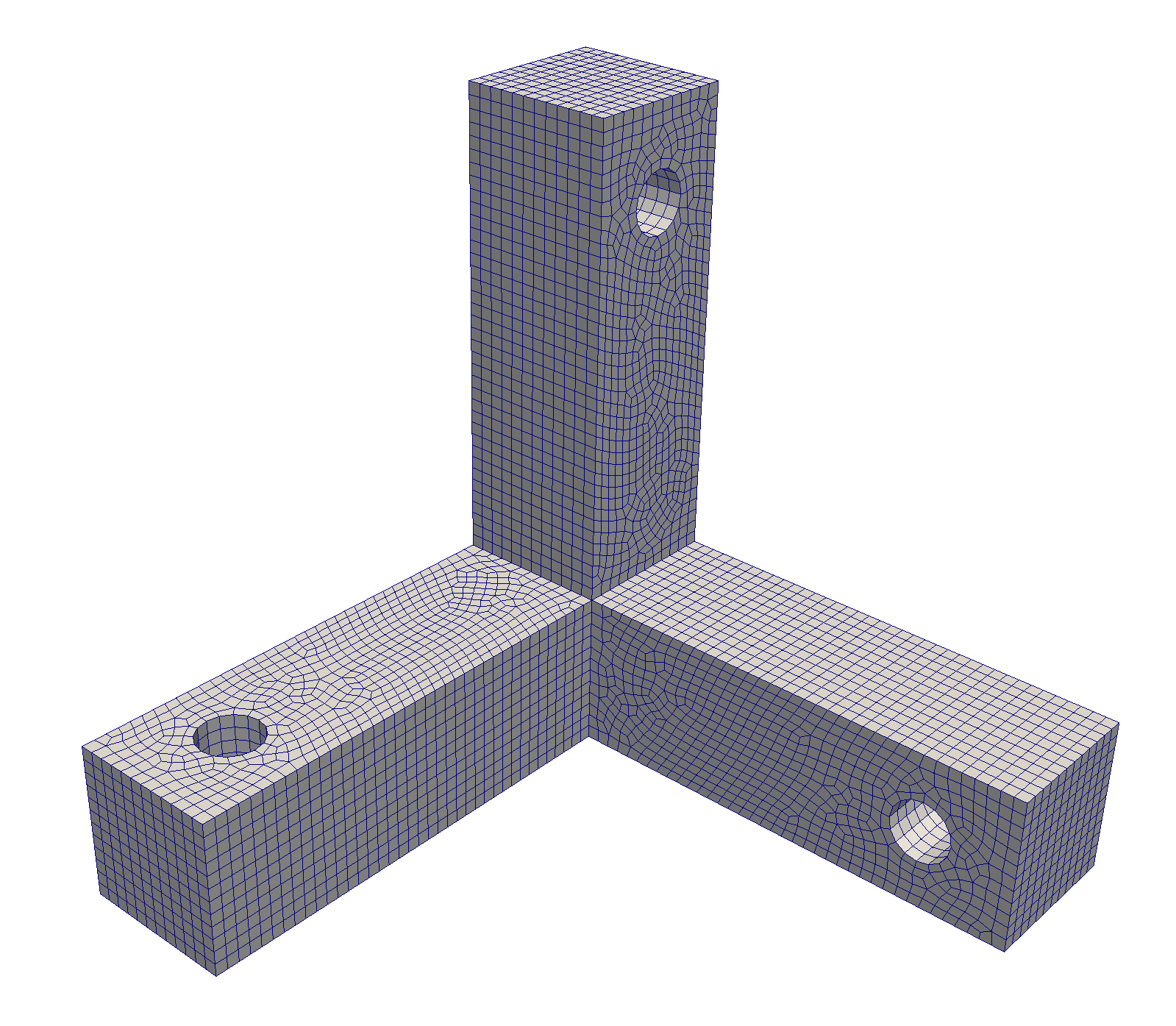
The orthogonal bracket is an interesting test case for topology optimization. It consists of three orthogonal, equally spaced members, with holes cut out in orthogonal directions. The following code performs the following steps:
Generates the orthogonal bracket geometry using egads4py’s solid boolean operations
Converts the egads4py objects to TMR-compatible geometry objects using
TMR.ConvertEGADSModelCollects all the TMR objects into a geometry model
geoUses TMR’s automatic coincident vertex, edge and face detection, and sweeping direction detection algorithm
TMR.setMatchingFaces(geos).Creates the coarse mesh with the call
mesh = TMR.Mesh(comm, geo). Note that the coarse mesh is created on the root processor and copied to all processors. This call will generate EGADS errorsEGADS Error: Edge/Sense not in Face (EG_getEdgeUV)!since different models are connected.Creates a model from the new mesh
model = mesh.createModelFromMesh(), and uses that model to generate the topology object required for the forest-of-octrees objecttopo = TMR.Topology(comm, model)Creates the forest of octrees
forest = TMR.OctForest(comm)Generates a random refinement and balances the mesh
Writes out the mesh to a file
The complete code is shown below:
from mpi4py import MPI
from egads4py import egads
from tmr import TMR
comm = MPI.COMM_WORLD
# Create the egads context
ctx = egads.context()
parts = []
r0 = 0.05
# Create the boxes
x0 = [0, 0, 0]
x1 = [0.25, 0.25, 0.25]
B0 = ctx.makeSolidBody(egads.BOX, rdata=[x0, x1])
parts.append(ctx.makeTopology(egads.MODEL, children=[B0]))
# Create the x-arm
x0 = [0.25, 0, 0]
x1 = [0.75, 0.25, 0.25]
B1 = ctx.makeSolidBody(egads.BOX, rdata=[x0, x1])
x0 = [0.85, 0.125, 0]
x1 = [0.85, 0.125, 0.25]
C1 = ctx.makeSolidBody(egads.CYLINDER, rdata=[x0, x1, r0])
parts.append(B1.solidBoolean(C1, egads.SUBTRACTION))
# Create the y-arm
x0 = [0, 0.25, 0]
x1 = [0.25, 0.75, 0.25]
B2 = ctx.makeSolidBody(egads.BOX, rdata=[x0, x1])
x0 = [0, 0.85, 0.125]
x1 = [0.25, 0.85, 0.125]
C2 = ctx.makeSolidBody(egads.CYLINDER, rdata=[x0, x1, r0])
parts.append(B2.solidBoolean(C2, egads.SUBTRACTION))
# Create the z-arm
x0 = [0, 0, 0.25]
x1 = [0.25, 0.25, 0.75]
B3 = ctx.makeSolidBody(egads.BOX, rdata=[x0, x1])
x0 = [0.125, 0, 0.85]
x1 = [0.125, 0.25, 0.85]
C3 = ctx.makeSolidBody(egads.CYLINDER, rdata=[x0, x1, r0])
parts.append(B3.solidBoolean(C3, egads.SUBTRACTION))
# Create all of the models
geos = []
for p in parts:
geos.append(TMR.ConvertEGADSModel(p))
# Create the full list of vertices, edges, faces and volumes
verts = []
edges = []
faces = []
vols = []
for geo in geos:
verts.extend(geo.getVertices())
edges.extend(geo.getEdges())
faces.extend(geo.getFaces())
vols.extend(geo.getVolumes())
# Set all of the matching faces
TMR.setMatchingFaces(geos)
# Create the geometry
geo = TMR.Model(verts, edges, faces, vols)
# Create the new mesh
mesh = TMR.Mesh(comm, geo)
# Set the meshing options
opts = TMR.MeshOptions()
opts.write_mesh_quality_histogram = 1
opts.triangularize_print_iter = 50000
# Create the surface mesh
htarget = 0.02
mesh.mesh(htarget, opts)
# Write the surface mesh to a file
mesh.writeToVTK('ortho_bracket.vtk', 'hex')
# Create the model from the unstructured volume mesh
model = mesh.createModelFromMesh()
# Create the corresponding mesh topology from the mesh-model
topo = TMR.Topology(comm, model)
# Create the quad forest and set the topology of the forest
forest = TMR.OctForest(comm)
forest.setTopology(topo)
# Create random trees and balance the mesh. Print the output file
forest.createRandomTrees(nrand=1, max_lev=3)
forest.balance(1)
filename = 'ortho_forest%d.vtk'%(comm.rank)
forest.writeForestToVTK(filename)